Dental X-rays are one of the easiest ways, and simple tools, for your dentist to peek beneath the surface. They can make you see what the eye cannot detect, concealed cavities, bone loss, infections and more.
If you’ve ever wondered why dentists rely on them or which types they wield, here’s an accessible and entertaining breakdown.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are Dental X-Rays?
Tooth X-ray or radiographs, are pictures of your teeth, gums, and jawbone that use only low levels of radiation. These images help dentists catch problems early, and often long before symptoms crop up. Unlike traditional pictures, X-rays show the inside of bones and teeth, allowing for thorough examination.
Despite the fact that for many people the word “X-ray” means nervousness, contemporary dental radiography is perfectly safe. Because of highly sophisticated equipment, digital sensors and radiation standards, the exposure is negligible, frequently inferior to what you receive on a short airplane ride.
What is the Importance of Tooth X-rays?
X-rays are an important tool in preventive dental care. Many oral issues start silently. With your vision, you may not experience pain or have symptoms until it is too late. That’s where X-rays can help; they provide a full view of what is going on inside your mouth.
1. Detecting Cavities You Can’t See
Cavities are not always visible on the surface. Some form between the teeth or beneath old fillings. X-rays enable the dentist to detect these early, stopping bigger, more expensive problems.
2. Monitoring Bone Health
X-rays tell your doctor about bone density and structure. This is especially crucial for those patients who suffer from periodontal disease, as bone loss can be monitored over time to monitor the extent of the condition.
3. Identifying Infections and Abscesses
One may not see an abscess in the mirror, but negative spaces on radiographs indicate where the infection has moved to around the root of a tooth.
4. Planning Dental Treatments
From braces to implants and root canals, dentists use tooth X-rays to plan treatments with precision. They depict teeth positions, jaw alignment and nerve pathways.
5. Checking Tooth Development in Children
For children and teenagers in particular, X-rays are crucial for monitoring the development of permanent teeth, detecting alignment issues and finding problems before they become significant.
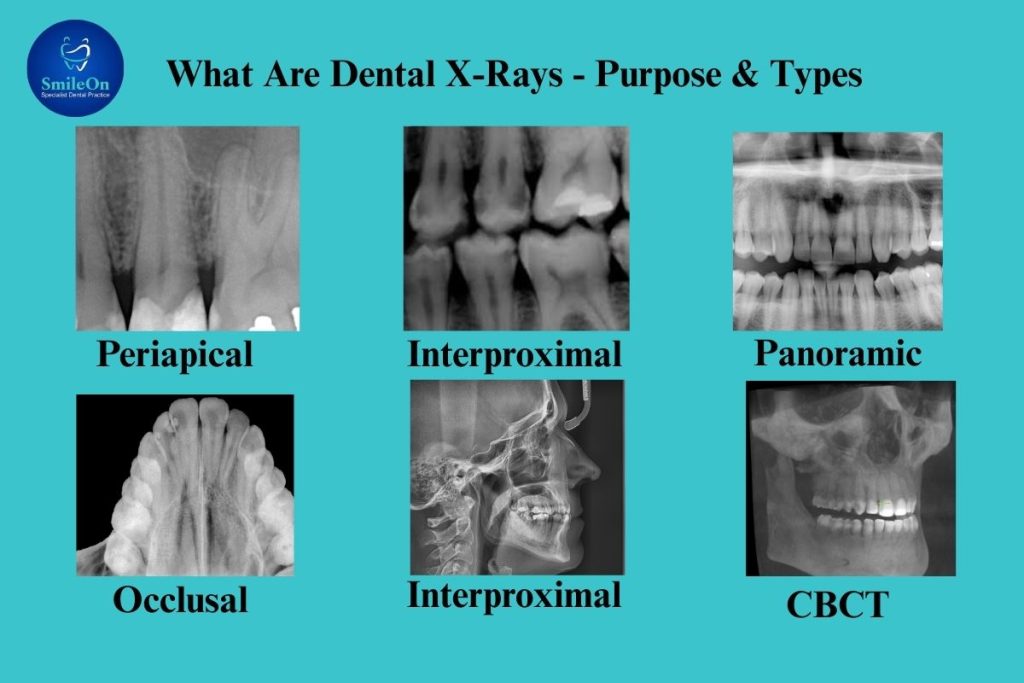
Types of Dental X-Rays
There is not one type of dental X-ray. When a dentist chooses the type, it depends on what they need to examine. Here’s a guide to the most common types:
Bitewing X-Rays:
Routine dental frequency x-rays are bitewings. As the sensor, which the doctor ill fit inside you mouth, gets your upper as well as lower teeth.
What They Show
- Cavities between teeth
- Below the gum line
- Decay under fillings
- Bone levels around teeth
Best For
- Regular examinations and early cavity detection.
Periapical X-Rays:
Shows one or two teeth from crown to root and surrounding bone. Hence, you can say that it allows dentist to focus on one tooth
What They Show
- Root infections
- Abscesses
- Fractures
- Impacted teeth
Best For
- Diagnosis of pain, planning of root canals or evaluation of tooth damage.
Panoramic X-Rays:
Whole-mouth X-rays can be taken with a full-mouth series or panoramic image. The machine whirls around your head to create a broad view.
What They Show?
- Wisdom teeth
- Jawbone problems
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
- Cysts and tumors
- Sinus structure
Best For
- Clinical constraints for treatment planning, orthodontics and evaluation of wisdom tooth position.
Occlusal X-Rays:
Occlusal views demonstrate structures of the floor or roof of the mouth. They are also bigger and tend to be used by kids.
What They Show
- Extra teeth
- Cysts
- Tooth development patterns
- Jaw fractures
Best For
- Children’s dental examinations and assessment of tooth development.
Cephalometric X-Rays:
Used for orthodontics, this X-ray takes a picture of the side view of the head, including jaw and teeth relation.
What They Show
- Jaw alignment
- Bite relationship
- Growth patterns
Best For
- Orthodontic analysis and planning, braces and Jaw Correction.
Cone Beam CT (CBCT) Scans:
A 3D X-ray, a CBCT scan, reveals the teeth, soft tissues, nerves and bones with great detail.
What They Show
- Precise bone structure
- Nerve pathways
- Jawbone thickness
- Implant placement areas
Best For
- Planning dental implants, complex surgeries, and assessing jaw disorders.
How Often Should I Get Dental X-Rays?
It is age, oral health, medical history and symptoms that dictate the frequency of taking dental x-ray. For example:
- The teeth and jaws of children are still growing, which means X-rays may be needed more frequently.
- A person with good oral health may only require them once every 1 to 2 years.
- People with gum disease, or a high frequency of cavities, are likely to need X-rays more frequently.
In addition to this, today’s digital X-rays produce 80–90% less radiation than the old type of film X-rays, so they are safe, even if taken more frequently for health reasons.
Why Do Children Need a Tooth X-ray?
Children might have X-rays more often, especially if they are prone to cavities or have alignment problems. X-rays help:
- Monitor erupting adult teeth
- Identify spot spacing or crowding issues early
- Cavities on the rise, which can happen in children
- Identify any jaw development issues
So, the more quickly we are able to identify dental problems, the better off your child’s mouth will be for healthy growth.
Purposes of Dental X-Rays
Dental X-rays equate to better oral care for many reasons, as follows:
Early Diagnosis:
The younger your kid is when dental issues are caught, the less susceptible they are to feeling pain, having infections and extractions or requiring expensive treatments.
Better Treatment Planning:
X-rays themselves, from fillings to orthodontics to implants, often provide informative scans that enable dentists to chart more accurate and effective courses of action.
Monitoring Changes Over Time:
Compare X-rays from different visits to look for changes such as bone loss, shifting teeth or healing after treatment.
Preventing Emergencies:
Finding these problems before they become a major issue can avoid unexpected dental emergencies like abscesses and broken teeth.
Aside from these specific advantages, though, dental X-rays allow dentists and patients alike to make well-informed decisions about the state of oral health. Being able to see the action below the gums helps make sense of recommended treatments and take preventive measures.
Ultimately, such early screenings will save your teeth and time, money and pain attending to problems when treatment can be delivered at the ground level.
Conclusion
They’re a window into your oral health. They reveal hidden problems, they guide treatment and, ideally, at least, help make sure you receive the best treatment available. Quick, safe and highly effective they play an important role in keeping your smile healthy for many years to come.
All in all, if the dentist recommends a set of X-rays, consider it a wise investment for your long-term oral health.