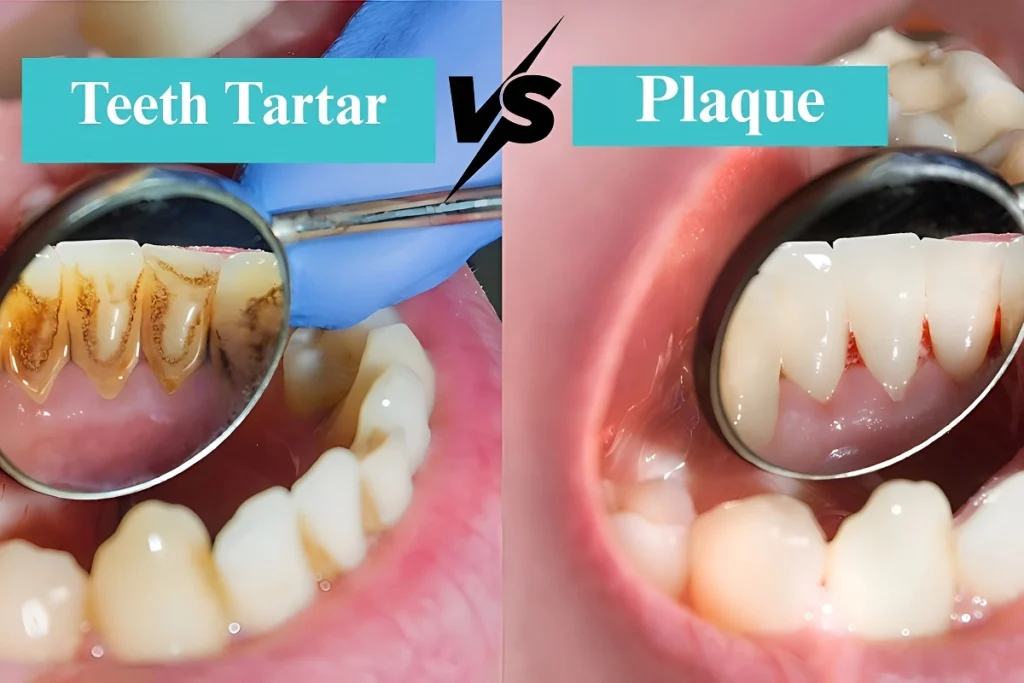
Brushing your teeth twice a day is not the only thing that keeps your teeth healthy; you should also learn what is accumulating in your teeth.
Plaque in teeth and dental tartar are two of the most common dental issues. These two conditions are quite different in terms of formation, risks and treatment, although many individuals assume that they are the same. Both can cause very serious oral health problems when inadequately attended to.
Keep reading as we are going to discuss the difference between plaque and tartar, their causes, and how they can be treated and prevented.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Tartar?
Dental tartar or calculus refers to a hardened plaque that attaches itself to your teeth and gums. It is hard; unlike soft plaque, which is removable by brushing teeth, tartar is hard and therefore is not easily removed without the help of a dentist.
Tartar that develops on the gum-line may be yellow or brown and may cause cosmetic and health concerns. Tartar accumulation occurs if you have ever felt like you had hard deposits on your teeth that cannot be removed by brushing your teeth.
In our guide what is Dental Calculus, you can read more about tartar in detail.
Causes of Tartar
The primary reason why tartar occurs is the inability to remove the plaque before it becomes hardened. The following are the main causes of tartar:
- Lack of oral hygiene: Not brushing or flossing the teeth means that plaque will become tartar.
- Sugar and starch diet: These foods promote the production of plaque, which becomes hardened as tartar.
- Dry mouth: Saliva will wash out bacteria; lack of saliva increases the risk of tartar.
- Smoking: These users of tobacco are resistant to the accumulation of tartar.
- Age and family history: There is a certain group of individuals who are more likely to have tartar.
What is Plaque?
Plaque is a sticky bacterial film that is constantly built on your teeth. In contrast to tartar, plaque is colorless and is difficult to notice unless you run your tongue over your teeth and feel that sticky stuff.
Plaque on the teeth is formed when the bacteria combine with the food particles, particularly the sugars and carbohydrates. This causes irritation to the gums and ultimately forms tartar when it is not removed on a daily basis.
Causes of Plaque
There are a number of health factors and daily habits that may cause excessive plaque:
- Poor brushing and flossing: When you don’t bother cleaning, bacteria stay and grow there.
- Sweet or sour foods and beverages: These are foods that support the bacteria in plaque.
- Unscheduled dental cleaning: Plaque in the hard-to-clean areas is removed by professional cleaning.
- Crowded teeth or misaligned teeth: make it difficult to remove plaque.
- Dehydration and dry mouth: Reduced saliva means that bacteria grow.
Plaque vs. Dental Tartar: What’s the Difference?
The terms plaque and tartar are not identical, though they are connected. We will take a closer look at their differences:
Formation & Texture:
- Plaque: Sticky, soft and can be easily removed by using normal brushing and flossing.
- Tartar: Calcified, hard, and firmly retained to teeth cannot be removed by the patient and will need to be removed by the professional.
Appearance:
- Plaque: This is usually not visible, although it can be felt as a fuzzy covering on teeth.
- Tartar: Can be seen as yellow, brown or even black. However, if you don’t treat them, they may leave dark spots. So, hit the link here to get to know how to remove black stains on teeth in detail.
Health Risks:
- Plaque: Results in cavities, bad breath and slight gum irritation when neglected.
- Tartar: You must know that tartar may form a calculus bridge once it becomes established. It is a dense mass of hardened deposits that connects two or more teeth. Hence, the cause of gum disease and tooth decay may happen, which can seriously damage the gums and tooth enamel.
Treatment Options
- Plaque: Brushing, flossing, and mouthwash are all easy to perform at home.
- Tartar: A dentist or hygienist has to polish it away using professional scaling apparatus.
Symptoms
- Plaque: Bad breath, slight redness of the gums, sensitivity and a filmy texture.
- Tartar: Swelling of the gums, bleeding of the gums, gums receding, and yellow hard deposits on the teeth.
A quick comparison table:
| Aspect | Plaque in Teeth | Dental Tartar |
| Formation & Texture | Soft, sticky film; easily removed with brushing and flossing. | Hard, calcified deposits; firmly attached and require professional cleaning. |
| Appearance | Usually invisible; may feel like a fuzzy coating. | Yellow, brown, or black deposits can cause black stains. |
| Health Risks | Can cause cavities, bad breath, and gum irritation. | Leads to gum disease, tooth decay, and may form dental calculus or a calculus bridge. |
| Treatment | Controlled with brushing, flossing, mouthwash, and diet. | It can be removed only by a dentist or a hygienist through scaling and cleaning. |
| Symptoms | Bad breath, mild gum redness, tooth sensitivity, filmy texture on teeth. | Gum swelling, bleeding gums, receding gum line, and hardened deposits on teeth. |
Plaque and Tartar Treatments
Treating Plaque:
- Fluoride toothpaste in the morning and evening.
- Flossing every day to floss between the teeth.
- Killing bacteria with mouthwash.
- Eating a low sugar/starch diet.
Treating Tartar:
- Dentists scrape tartar off with scrapers.
- In severe cases, the surfaces of the roots are smoothed to avoid the accumulation of bacteria.
- Checking your dentist every 6 months will help you to avoid the build-up of tartar.
Conclusion
Plaque and tartar are similar; however, the difference between them can be the difference between a healthy smile and dental issues that hurt. The soft, invisible film, which forms every day, is called plaque, and the hardened, more dangerous form, which can be removed only by your dentist, is called tartar.
With good oral hygiene, eating habits, and regular check-ups at SmileOn, where your smile is truly taken care of, you can avoid the destruction of your teeth. Keep in mind: long-term oral health is achieved by taking small steps each day.
Waiting until plaque turns into tartar is not the way to go. Take care of your teeth today and have a better and healthier smile tomorrow.
FAQs
What are the complications of plaque?
Failure to remove plaque regularly may lead to cavities, bad breath, tooth sensitivity, and gum disease. With time, untreated plaque becomes hardened into tartar that is harder to control.
What happens if tartar is not removed?
When tartar is not treated, it may cause inflammation of the gum, periodontal disease, loss of bone and even loss of teeth.
Can teeth fall out after tartar removal?
No, teeth do not fall after cleaning tartar. As a matter of fact, professional cleaning enhances your oral health. But when the accumulation of tar has already led to serious gum disease and bone loss, the loss of teeth may follow with time.
However, it is not due to the cleaning procedure, but due to late treatment.