When we think about oral health, the first things that probably come to mind are cavities or toothaches.
But did you know that your gums have an equally big role in maintaining a healthy, happy smile?
One of the most widespread problems involving the gum line is gingivitis, something that can begin quietly but lead to serious dental issues if it remains unchecked. The good news? Gingivitis can be reversed with proper care and treatment.
Let’s know what gingivitis is, its symptoms and treatments. By the end, you will be sure when to get swollen gums treatment, how to prevent it, and how it differs from more advanced gum disease.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Gingivitis?
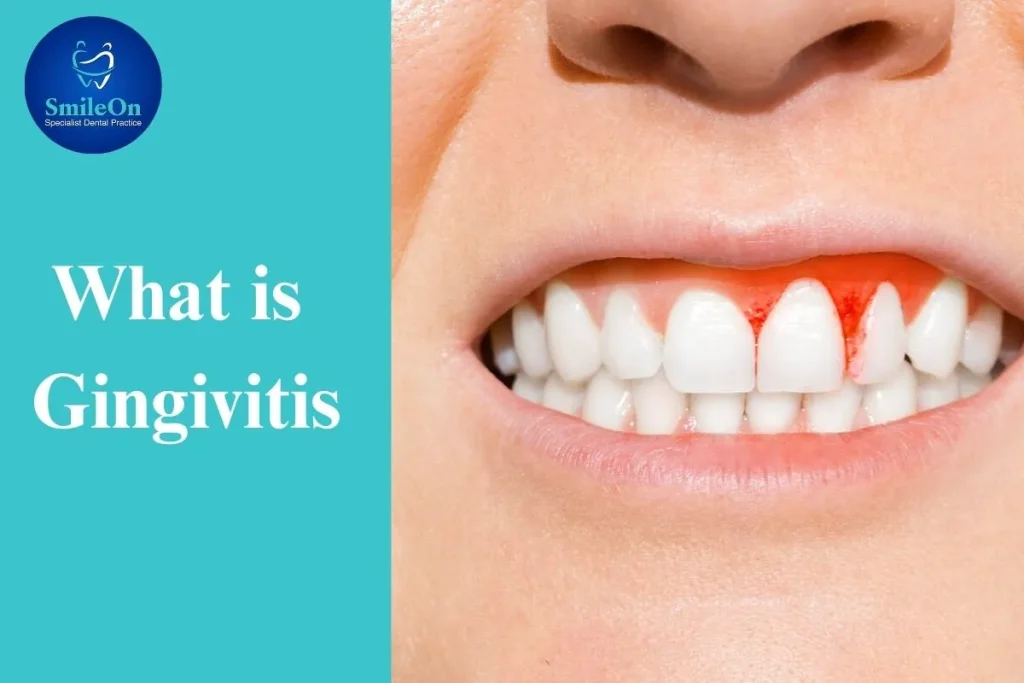
Gingivitis is the mildest form of periodontal disease. It happens when plaque, a film of bacteria that sticks to the teeth, irritates the gums. This causes gum tissue to become inflamed, red and swollen. Unlike more severe types of gum disease, known as periodontitis, gingivitis doesn’t result in any permanent damage to the bone or tissue that holds your teeth in place.
It is a very common problem that can affect people of any age. Nonetheless, it is more commonly observed in adult people because of lifestyle choices, bad oral habits and certain health disorders. Although gingivitis by itself might appear minor, untreated, it can develop into periodontitis. It is a more advanced form of gum disease that may eventually result in tooth loss.
All in all, gingivitis is a way for your gums to warn you that they need better treatment.
Periodontitis vs Gingivitis: What’s the Difference?
One question that patients often ask is: What’s the difference between gum and periodontal disease?
- Gingivitis: Early stage of gum disease. It affects only the gums and is marked by redness, swelling and bleeding. The bone and connective tissue are preserved, however. Gingivitis is curable by treatment.
- Periodontitis: A more severe form of gum disease when gingivitis goes unchecked. It also erodes the foundation of the teeth, such as the bone. It is characterized by deep gum pockets, receding gums, loose teeth, and even tooth loss. Unlike with gingivitis, periodontitis results in permanent damage and requires more aggressive treatment.
Gingivitis could be thought of like a warning light. If you catch it early, then your gums and teeth can be saved. Left untreated, the condition progresses into periodontitis, which is harder and more expensive to treat.
Most Common Gingivitis Symptoms
It is important to identify the symptoms of gingivitis in time so that you can avoid further serious dental issues. The bad news is that too often, people ignore gum issues or consider it as a side effect of brushing aggressively when, in fact, these are warning signs.
Here are some common signs of gingivitis:
- Swollen or puffy gums: One of the first symptoms you can easily see. Gums may be sensitive or painful to touch. Look for an effective gum swelling treatment as soon as possible, for healthier gums and teeth.
- Gums that turn red: Your gums should be pinkish in color. If they appear dark red or purple, it’s a sign of inflammation.
- Bleeding between teeth: You might feel like something is stuck in your teeth, but you can’t get it out. This is often a sign of gingivitis.
- Bad breath (halitosis): Build-up of bacteria can result in chronic bad breath even after you have brushed your teeth.
- Sensitive gums: You may experience discomfort with eating, brushing, and flossing.
- Receded gums: Sometimes, gingivitis can lead to the gum line receding a little.
- Soft gums: Gums can also be mushy in texture, soft, or might have lost their firmness.
If you do experience these symptoms, you should see a dentist as soon as possible. Early treatment of gingivitis can help reverse the condition before your gums develop into something more serious.
Major Causes of Gingivitis
To know how to prevent and treat gingivitis, you should first understand its causes. The chief offender is plaque, of course, but a number of contributory factors can up your risk.
Poor Oral Hygiene:
If you don’t brush and floss well, plaque can build up. Plaque eventually hardens into tartar that can only be removed by a dentist.
Smoking and Tobacco Use:
Tobacco products break down your gums’ ability to heal and allow bacteria to flourish.
Poor Diet:
Without the proper vitamins, particularly Vitamin C for enhanced immunity, gums are more prone to infection and inflammation.
Hormonal Changes:
The sensitivity of the gums and the risks for gingivitis can increase during pregnancy, menstruation or menopause.
Medical Conditions:
Illnesses such as diabetes, HIV and those that compromise immunity can make you more vulnerable to gum disease.
Medications:
Some medications dry the mouth and reduce saliva flow, so bacteria can get out of control.
Genetics:
Following the traditional dental advice and adequate flossing is a must, especially for those who come from families that are genetically susceptible to gum disease.
The most common cause is still poor oral hygiene. But, as you can see, gingivitis is often a product of a combination of lifestyle and health factors.
Types of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is not a one-size-fits-all condition. Dentists divide it into various types based on the cause and severity.
Plaque-Induced Gingivitis:
This is the most frequent kind, directly due to the accumulation of plaque on teeth and gums.
Non-Plaque-Induced Gingivitis:
In other cases, gingivitis may result from something other than plaque, including:
- Viral or fungal infections
- Allergies (to dental products, toothpastes or mouthwashes).
- Genetic conditions
- Systemic diseases
Hormonal Gingivitis:
Observe in young pregnant females, teenagers, or during menopause with hormonal changes.
Medication-Induced Gingivitis:
Some medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure or prevent seizures, can cause gums to swell.
If the cause of a case of gingivitis is known, a dentist can suggest what type of gum swelling treatment will most benefit the patient.
Gingivitis Treatment Options
The good news is that gingivitis can be reversed if treated early. Swollen gums treatment or other gingivitis treatments are used to heal the gums and eliminate infection and inflammation.
The following are the best treatments out there for gingivitis:
Professional Dental Cleaning:
Your dentist or dental hygienist will use scaling and root planing to get rid of plaque and tartar. This deep cleaning cuts down on bacteria and gives your gums a chance to heal.
Improved Oral Hygiene:
At-home care is just as significant as professional care. This includes:
- Twice daily brushing with a fluoride toothpaste
- Daily flossing to clean plaque particles lodged between your teeth
- Rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash to fight off germs
Medications:
According to the severity, dentists may recommend:
- Antibiotic gels or mouth rinses
- Chips of antiseptic in gum pockets
- Oral antibiotics for severe infections
Lifestyle Changes:
Kicking the smoking habit, eating more healthfully and keeping conditions such as diabetes in check are essential for long-term gum health.
Surgical Options (for Advanced Cases):
When gingivitis becomes periodontitis, you might need procedures such as flap surgery, bone grafts or guided tissue regeneration.
If you have inflamed gums, be sure to take swift action to treat swollen gums. If treated early on, gingivitis can be completely reversed and no tooth loss or additional oral health concerns will occur.
FAQs
Can a general dentist treat gingivitis?
Yes, gingivitis can be diagnosed and treated by a general dentist with professional cleaning, medications and instruction on proper oral hygiene. If the condition advances to periodontitis, they will recommend a periodontist (gum specialist).
Do gingivitis go away on its own?
No, gingivitis does not just go away. Good oral care can help alleviate the symptoms, but if it has calcified, then likely you will need a professional cleaning for it to be removed. Gingivitis often develops into periodontitis when left untreated.
How to tell if gingivitis is healing?
These healing indicators would include less bleeding, decreased redness and swelling, freshening breath or gums that feel tighter and fit snug around the teeth. Brushing and flossing regularly along with taking your dentist’s advice to heart are key to recovering.
Final Thoughts
Gingivitis can often start with just a little bit of bleeding or mild swelling, but it should never be ignored. It’s the body’s way of telling you to pay attention to your gums. The good news is that if you get gingivitis treatment in time and make your dental appointments, not only can you restore your gums to a healthy state, but you can prevent this from ever happening again.
As always, healthy gums mean strong teeth and a beautiful smile. Don’t put off having a dental check-up if you have these symptoms. Schedule your appointment with a professional dentist at SmileOn and get healthy gums and teeth!